AngularJS is an
open source JavaScript MVC framework for web application or web sites. It
extends the HTML and makes it dynamic. AngularJS can be used to create Single
Page Applications.
AngularJS is a very powerful JavaScript
Framework. It is used in Single Page Application (SPA) projects. It extends
HTML DOM with additional attributes and makes it more responsive to user
actions. AngularJS is open source, completely free, and used by thousands of
developers around the world. It is licensed under the Apache license version
2.0.
AngularJS
Architecture
Angular.js follows
the MVC architecture, the diagram of the MVC framework as shown below.
v The Controller represents the layer that has the business logic. User events trigger the functions which are stored inside your controller. The user events are part of the controller.
v Views
are used to represent the presentation layer which is provided to the end users
v Models
are used to represent your data. The data in your model can be as simple as
just having primitive declarations. For example, if you are maintaining a
student application, your data model could just have a student id and a name.
Or it can also be complex by having a structured data model. If you are
maintaining a car ownership application, you can have structures to define the
vehicle itself in terms of its engine capacity, seating capacity, etc.
Applications of AngularJS
The general features of AngularJS are as follows :
v AngularJS is a efficient framework that can create Rich Internet Applications (RIA).
v AngularJS provides developers an options to write client side applications using JavaScript in a clean Model View Controller (MVC) way.
v Applications written in AngularJS are cross-browser compliant. AngularJS automatically handles JavaScript code suitable for each browser.
v AngularJS is open source, completely free, and used by thousands of developers around the world. It is licensed under the Apache license version 2.0.
v Overall, AngularJS is a framework to build large scale, high-performance, and easyto-maintain web applications.
Setup
AngularJS Development Environment
We
need the following tools to setup a development environment for AngularJS:
v AngularJS Library
v Editor/IDE
v Browser
v Web server
AngularJS Library
To download AngularJS library, go to angularjs.org
click download button, which will open the following popup.
Download AngularJS Library
Select the required
version from the popup and click on download button in the popup.
Editor
AngularJS is eventually HTML and JavaScript code. So you can install any good editor/IDE as per your choice.
The following editors are recommended:
v Eclipse
AngularJS
Advantages
v
Two-way binding –
Angular.js keeps the data and presentation layer in sync. Now you don't need to
write additional JavaScript code to keep the data in your HTML code and your
data later in sync. Angular.js will automatically do this for you. You just
need to specify which control is bound to which part of your model.
v Routing – Angular can take care of routing which means moving from one view to another. This is the key fundamental of single page applications; wherein you can move to different functionalities in your web application based on user interaction but still stay on the same page.
v Angular supports testing, both Unit Testing, and Integration Testing.
v It extends HTML by providing its own elements called directives. At a high level, directives are markers on a DOM element (such as an attribute, element name, and comment or CSS class) that tell AngularJS's HTML compiler to attach a specified behavior to that DOM element. These directives help in extending the functionality of existing HTML elements to give more power to your web application.
There are several benefits as listed below:
Dependency Injection
In software engineering,
dependency injection refers to the passing of objects between the application
and the client.
Injection is the phenomenon of
passing a dependency (say an application service) to a dependent object (say a
client) that would use it. AngularJS provides several core components for
achieving this purpose in simplicity.
Model View
Controller
AngularJS is used to create Rich Internet Applications (RIA), and two-way
data binding is achievable due to the MVC (model view controller) architecture
in Angular JS.
A basic depiction of this architecture is as shown below:
MVC Model
for AngularJS
As developers, we just have to split our code into the model, view, and
controller and the rest of the operations such as managing the components and
connecting them together will be automatically done by AngularJS.
Two-way Data
Binding
Software changes should be responsive, and changes within the system
should be catered to the changes in the user interface and conversely, with
precision and speed.
AngularJS offers this kind of binding by synchronizing between the model
and the view.
Testing
It is interesting to know the fact that AngularJS was designed keeping
testing in mind, right from the beginning.
Any of the components of AngularJS can be comfortably tested using both
unit testing and an end to end testing. The application can be transported
across browsers for testing purposes.
Controlling the behavior of DOM elements
Attributes of AngularJS can be linked to directives so that automatic
initialization of the application is possible.
This means that there is modularity in AngularJS and with the help of its
features such as directives and filters, a sense of customization and
flexibility can be achieved in the code.
Now, we have seen the answers to all the why- questions that may arise as
a result of apprehensions in learning something new, and I think we’re good to
go.
It is always better to learn a technological trend and keep updating
ourselves often to make the most out of our careers and also to keep that
inquisitive mind of ours always thirsty for knowledge.
$scope in AngularJS is a built-in object which basically binds
the "controller" and the "view". One can define member
variables in the scope within the controller which can then be accessed by the
view.
Consider example below:
angular.module('app',[]).controller('HelloWorldCntrl' function($scope) { $scope.message = "Hello World" });
Code Explanation:
v The name of the module is "app"
v The name of the controller is "HelloWorldCntrl"
v Scope object is the main object which is used to pass information from the controller to the view.
v Member variable added to scope object
HTML code with some strange attributes and braces such as ng-app, ng-model, and {{ }}. These built-in attributes in AngularJS are called directives.
The following figure illustrates the AngularJS building blocks in the above example.
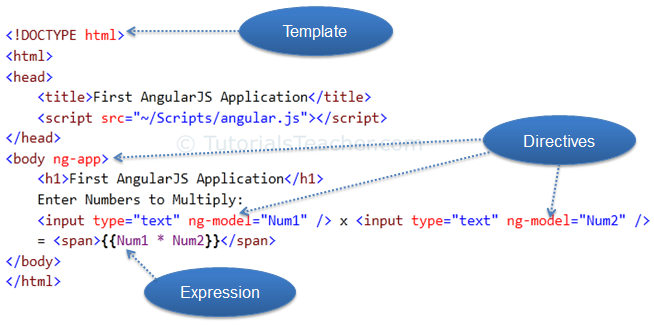
Template
In AngularJS, a template is HTML with additional
markups. AngularJS compiles templates and renders the resultant HTML.
Directive
Directives are markers (attributes) on a DOM
element that tell AngularJS to attach a specific behavior to that DOM element
or even transform the DOM element and its children.
Most of the directives in
AngularJS are starting with ng.
It stands for Angular. We have applied ng-app and ng-model directive in the
above example.
ng-app: The ng-app directive is a starting point. If
AngularJS framework finds ng-app directive anywhere in the HTML document then
it bootstraps (initializes) itself and compiles the HTML template.
ng-model: The ng-model directive binds HTML element to a
property on the $scope object.
You will learn about this model later but for now let us consider this as a
model property.
In the above example, we have
included ng-model directive to both the textboxes with different names Num1 and
Num2. AngularJS framework will create two properties called Num1 and Num2 in
the scope and will assign a value that we type into textboxes.
Expression
An expression is like JavaScript code which is
usually wrapped inside double curly braces such as {{ expression }}. AngularJS
framework evaluates the expression and produces a result. In the above example,
{{ Num1 * Num2}} will simply display the product of Num1 and Num2.
The following table lists all the important concepts in AngularJS.
|
Concept |
Description |
|
Template |
HTML with additional markup |
|
Directives |
Extends the HTML with custom attributes and
elements |
|
Model |
The data shown to the user in the view and with
which the user interacts |
|
Scope |
A context where the model is stored so that
controllers, directives and expressions can access it |
|
Expressions |
Executes JavaScript code inside brackets {{ }}. |
|
Compiler |
Parses the template and instantiates directives
and expressions |
|
Filter |
Formats the value of an expression for display to
the user |
|
View |
what the user sees (the DOM) |
|
Data Binding |
Sync data between the model and the view |
|
Controller |
Maintains the application data and business logic |
|
Module |
a container for different parts of an app
including controllers, services, filters, directives which configure the
Injector |
|
Service |
Reusable business logic, independent of views |
|
Dependency Injection |
Creates and wires objects and functions |
|
Injector |
Dependency injection container |
AngularJS
Directives
Directives are
markers on a DOM element that tell AngularJS to attach a specified behavior to
that DOM element or even transform the DOM element and its children. In short,
it extends the HTML.
Most of the directives in AngularJS are starting with ng- where ng stands for Angular.
AngularJS includes various built-in directives. In addition to this, you can
create custom directives for your application.
The following table lists the important built-in
AngularJS directives.
|
Directive |
Description |
|
ng-app |
Auto
bootstrap AngularJS application. |
|
ng-init |
Initializes
AngularJS variables |
|
ng-model |
Binds
HTML control's value to a property on the $scope object. |
|
ng-controller |
Attaches
the controller of MVC to the view. |
|
ng-bind |
Replaces
the value of HTML control with the value of specified AngularJS expression. |
|
ng-repeat |
Repeats
HTML template once per each item in the specified collection. |
|
ng-show |
Display
HTML element based on the value of the specified expression. |
|
ng-readonly |
Makes
HTML element read-only based on the value of the specified expression. |
|
ng-disabled |
Sets
the disable attribute on the HTML element if specified expression evaluates
to true. |
|
ng-if |
Removes
or recreates HTML element based on an expression. |
|
ng-click |
Specifies
custom behavior when an element is clicked. |
ng-app
The ng-app directive initializes AngularJS and makes the specified element a root element of the application. Visit ng-app section for more information.
ng-init
The ng-init directive can be used to initialize variables
in AngularJS application.
ng-model
The ng-model directive is used for two-way data binding in
AngularJS. It binds <input>, <select> or <textarea> elements
to a specified property on the $scope object. So, the value of the element will
be the value of a property and vica-versa.
ng-bind
The ng-bind directive binds the model property declared
via $scope or ng-model directive or the result of an expression to the HTML
element. It also updates an element if the value of an expression changes.
ng-repeat
The ng-repeat directive repeats HTML once per each item
in the specified array collection.
ng-repeat is used with students array. It
creates <li> element for each item in the students array. Using the same
way it repeats the <div> element.
ng-if
The ng-if directive creates or removes an HTML element based on the
Boolean value returned from the specified expression. If an expression returns
true then it recreates an element otherwise removes an element from the HTML
document.
ng-readonly
The ng-readonly directive makes an HTML element
read-only, based on the Boolean value returned from the specified expression.
If an expression returns true then the element will become read-only, otherwise
not.
ng-disabled
The ng-disabled directive disables an HTML element, based
on the Boolean value returned from the specified expression. If an expression
returns true the element will be disabled, otherwise not.
Directive Syntax
AngularJS
directives can be applied to DOM elements in many ways. It is not mandatory to
use ng- syntax only.
Directive can
start with x- or data-, for example ng-model directive can be written as
data-ng-model or x-ng-model.
Also, the - in the
directive can be replaced with : or _ or both. For example, ng-model can be
written as ng_model or ng:model. It can also be a mix with data- or x-.
AngularJS
Controller
You can attach properties and methods to the $scope object inside a controller function, which in turn will add/update the data and attach behaviours to HTML elements. The $scope object is a glue between the controller and HTML.
The ng-controller directive is used to specify a controller in HTML element, which will add behavior or maintain the data in that HTML element and its child elements.
Scope in
AngularJS
The $scope in an AngularJS is a built-in object, which
contains application data and methods. You can create properties to a $scope
object inside a controller function and assign a value or function to it.
The $scope is glue between a controller and view (HTML).
It transfers data from the controller to view and vice-versa.
As we have seen in the
controller section, we can attach properties and methods to the $scope object
inside controller function. The view can display $scope data using an
expression, ng-model, or ng-bind directive, as shown below.
AngularJS creates and injects a
different $scope object to each controller in an application. So, the data and
methods attached to $scope inside one controller cannot be accessed in another
controller. With the nested controller, child controller will inherit the
parent controller's scope object. Therefore, child controller can access
properties added in parent controller but parent controller cannot access
properties added in child controller.
An AngularJS application has a single $rootScope. All the other $scope
objects are child objects.
The properties and methods attached to $rootScope will be
available to all the controllers.
The following example
demonstrates the $rootScope and $scope object.
The $scope object
contains various methods. The following table lists important methods of $scope
object.
|
Method |
Description |
|
$new() |
Creates
new child scope. |
|
$watch() |
Register
a callback to be executed whenever model property changes. |
|
$watchGroup() |
Register
a callback to be executed whenever model properties changes. Here, specify an
array of properties to be tracked. |
|
$watchCollection() |
Register
a callback to be executed whenever model object or array property changes. |
|
$digest() |
Processes
all of the watchers of the current scope and its children. |
|
$destroy() |
Removes
the current scope (and all of its children) from the parent scope. |
|
$eval() |
Executes
the expression on the current scope and returns the result. |
|
$apply() |
Executes
an expression in angular outside the angular framework. |
|
$on() |
Register
a callback for an event. |
|
$emit() |
Dispatches
the specified event upwards till $rootScope. |
|
$broadcast() |
Dispatches
the specified event downwards to all child scopes. |
$watch
Angular scope object includes $watch event which will be raised whenever
a model property is changed.
AngularJS
Events
AngularJS includes
certain directives which can be used to provide custom behavior on various DOM
events, such as click, dblclick, mouseenter etc.
The following table
lists AngularJS event directives.
|
Event Directive |
|
ng-blur |
|
ng-change |
|
ng-click |
|
ng-dblclick |
|
ng-focus |
|
ng-keydown |
|
ng-keyup |
|
ng-keypress |
|
ng-mousedown |
|
ng-mouseenter |
|
ng-mouseleave |
|
ng-mousemove |
|
ng-mouseover |
|
ng-mouseup |
<head><scriptsrc="~/Scripts/angular.js"></script>
</head><bodyng-app="myApp">
<divng-controller="myController">
Enter Password:<inputtype="password"ng-model="password"/><br/>
<buttonng-click="DisplayMessage(password)">Show Password</button
</div>
<script>
varmyApp = angular.module('myApp', []);
myApp.controller("myController",function($scope, $window) {
$scope.DisplayMessage =function(value) {
$window.alert(value) } });</script>
</body>
<body ng-app>
<div ng-class="{redDiv: enter, yellowDiv: leave}" ng-mouseenter="enter=true;leave=false;"
ng-mouseleave="leave=true;enter=false">
Mouse <span ng-show="enter">Enter</span> <span ng-show="leave">Leave</span>
</div>
</body>
AngularJS Service
AngularJS services are JavaScript functions for specific tasks, which can be reused throughout the
application.
AngularJS includes services for different purposes. For example, $http service can be used to send
an AJAX request to the remote server. AngularJS also allows you to create
custom service for your application.
Most AngularJS services interact with the controller, model or custom directives. However,
some services interact with view (UI) also for UI specific tasks.

The following table lists all the built-in AngularJS services.
$anchorScroll $exceptionHandler $interval $rootScope $animate $filter $locale $sceDelegate $cacheFactory $httpParamSerializer $location $sce $templateCache $httpParamSerializerJQLike $log $templateRequest $compile $http $parse $timeout $controller $httpBackend $q $window $document $interpolate $rootElement
All the Angular services are lazy instantiated and singleton. It means AngularJS framework instantiates a service when an application component
depends on it. Also, all the components share the same instance of a service.
$http Service
The $http service is used to send or receive data from the remote server using browser's XMLHttpRequest or JSONP.
$http is a service as an object. It includes following shortcut methods.
Method Description $http.get() Perform Http GET request. $http.head() Perform Http HEAD request. $http.post() Perform Http POST request. $http.put() Perform Http PUT request. $http.delete() Perform Http DELETE request. $http.jsonp() Perform Http JSONP request. $http.patch() Perform Http PATCH request.
$http.get()$http.get() method sends http GET request to the remote server and retrieves the data.
Signature: HttpPromise $http.get(url)
$http.get() method returns HttpPromise object, which includes various methods to process the response of http GET request.
The following example demonstrates the use of $http
service in a controller to send HTTP GET request.







No comments:
Post a Comment